

Blog: Successful test with GridShield via power line communication
By: Bart Nijenhuis, PhD candidate at University of Twente
Recently, researchers within the SmoothEMS with GridShield project conducted a field test using the GridShield algorithm. In previous field tests, GridShield control signals were sent using LoRa (LoRa for Long Range) technology, a wireless network that can send and receive signals between sensors or actuators. However, this new field test uses a digital power line communication technique. With this technique, the GridShield control signal is transferred through the power line itself. From within a transformer in the local grid, a signal is produced and sent to every device connected to the transformer via the neutral power line. Connected devices, equipped with a small receiver, can act on the received signal when necessary, for example when the load of the transformer is approaching its limits. In this field test, the digital power line communication sender was installed in a nearby building that acted as transformer. Figure 1 shows the smart solar charging station at the field test location.

In the field test with the power line communication, the GridShield algorithm was used to control an electric vehicle charging hub equipped with multiple EV charging stations and a solar PV power installation. The main objective of the setup is to robustly control the EV charging stations to prevent overloading of the local grid due the combined power consumption of all assets present. Measurements at the building level were used as a reference for the algorithm, thus including the PV power production in combination with the EV charging power. The results show a quick response time of the whole setup: in under two seconds, the charging stations respond to a command sent through the power line communication from inside the building by decreasing or increasing their available charging power, as shown in Figure 2.
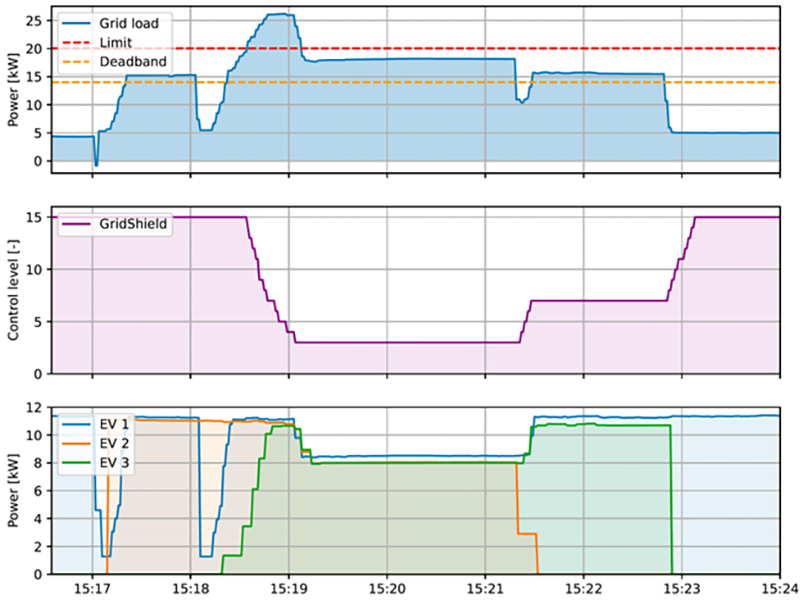
Figure 2 shows the result of the test. Just after 15:17, EV 2 (orange) starts to charge in addition to EV 1 (blue). The value of the grid load is now just above the deadband, so no control signal has to be applied. One minute later, EV 3 starts, causing the grid load to surpass the limit. GridShield immediately responds by lowering the control level until the load is between the limit and the deadband. All EVs are now curtailed at around 8 kW. Just after 15:21, EV 3 leaves the charging station. Now, more capacity is available for the other two charging stations: GridShield again immediately responds by increasing the control level so that this capacity is made available for the other charging stations.
The test demonstrates the working principle of GridShield and verifies its compatibility with the DigitalPLC power line communication technology, with adequate response times for use in this type of environments and applications. The system has shown to be an interesting and suitable technology to act as a grid overload protection mechanism and as a fast communication technology for energy management purposes. The measured performance for these appliations is comparable to the LoRa communication previously used in the GridShild project.
We would like to thank to thank owners and staff at Frans op den Bult in Deurningen (for their hospitality at the test location), Smart State Technology (for relying on their measurement equipment already installed at the test location) and FlinterCS for supplying the DigitalPLC technology.







